Transformer Network in Pytorch from scratch
Published:
Step by step implementation of “Attention is all you need” with animated explanations.
This is a supplementary post to the medium article Transformers in Cheminformatics.
Code
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import math, copy, time
from torch.autograd import Variable
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# import seaborn
from IPython.display import Image
import plotly.express as px
# seaborn.set_context(context="talk")
%matplotlib inline
Single headed dot-scaled attention
\[Attention(Q,K,V) = softmax(\frac{QK^T}{\sqrt {d_k}})V\]Image(filename='./Images/self_attn.png',width=1000)
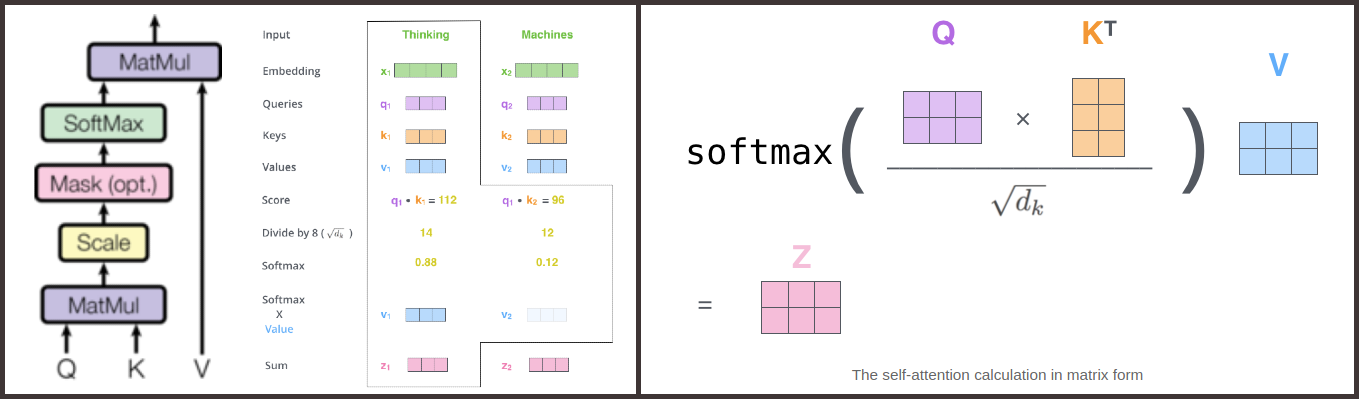
def attention(query, key,value, mask = None,dropout = None): #query:Q, key: K, value: V
dk = key.shape[-1]
score = torch.matmul(query,key.transpose(-1,-2)) #BxLxD
scaled_score = score/math.sqrt(dk)
#Masking (optional)
#Increase score to very large negative number for tokens that are masked.
#Such large negative number will have 0 exponentiation and hence their softmax will be 0 as well.
if mask is not None:
scaled_score.masked_fill(mask==0,-1e9)
attention = F.softmax(scaled_score,dim=-1)
#Optional: Dropout
if dropout is not None:
attention = nn.Dropout(attention,dropout)
#Z = enriched embedding
Z = torch.matmul(attention,value)
return Z, attention
Image(filename='./Images/multiheaded_attn.png',width=850)
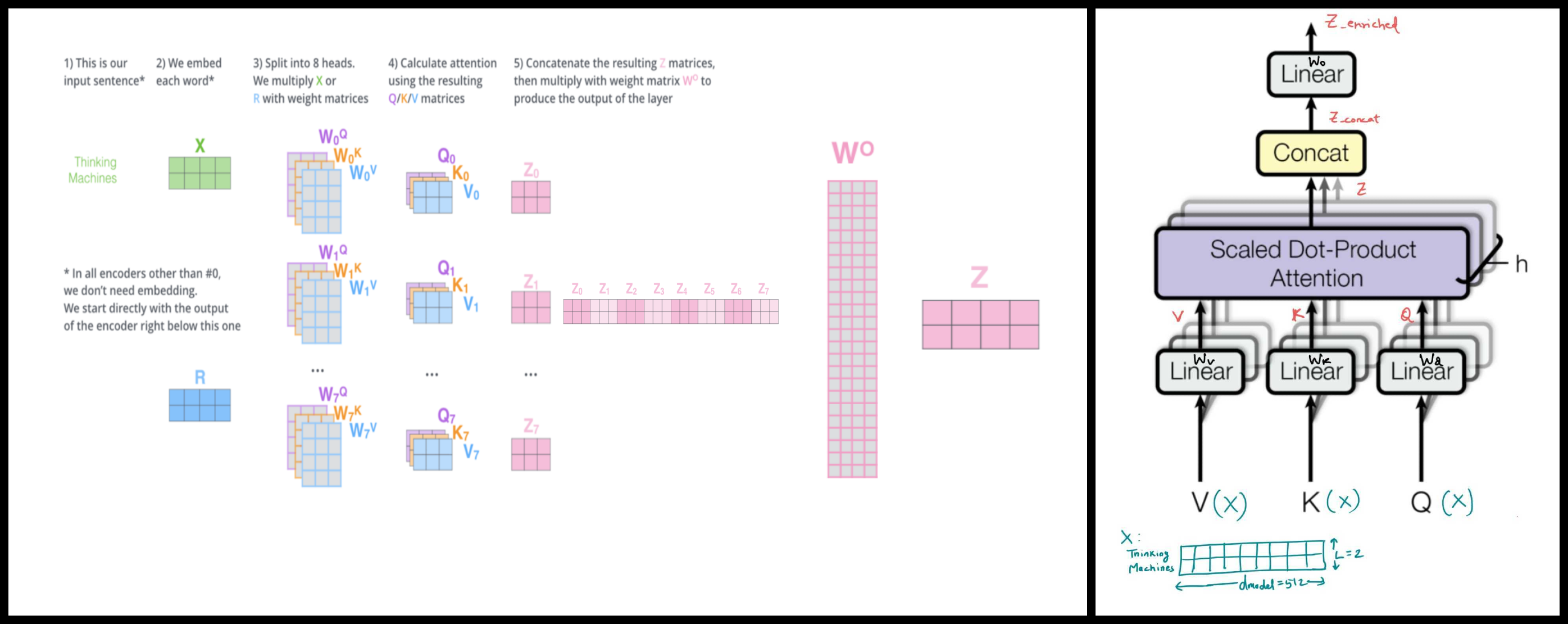
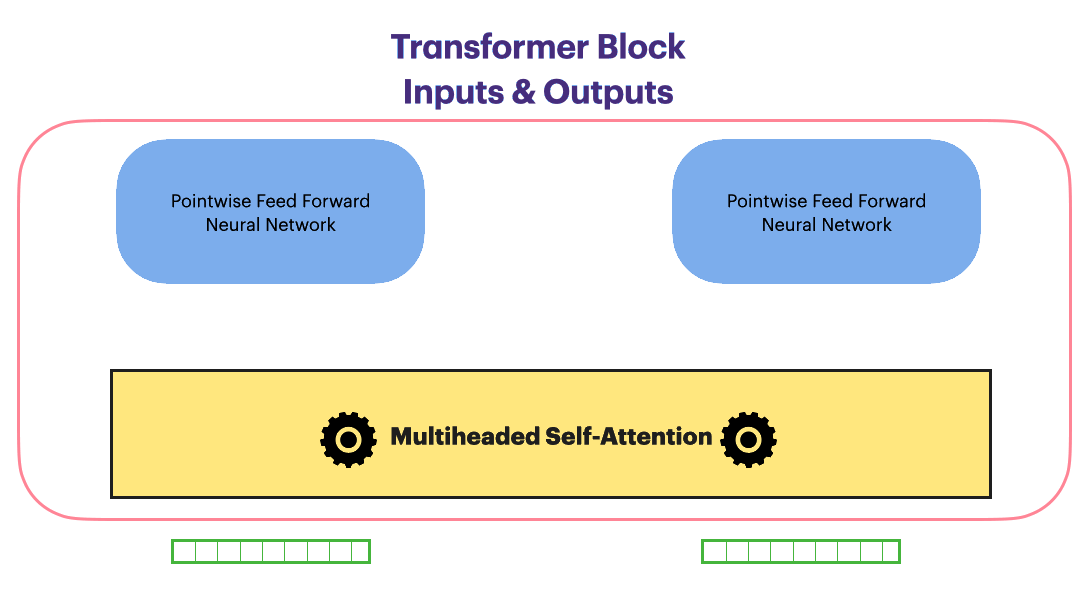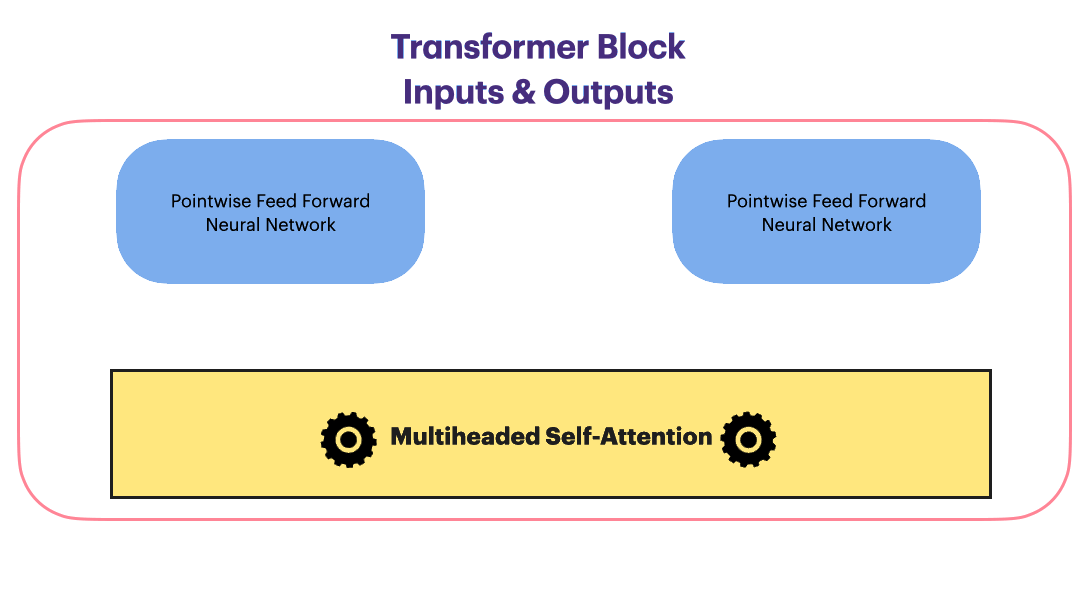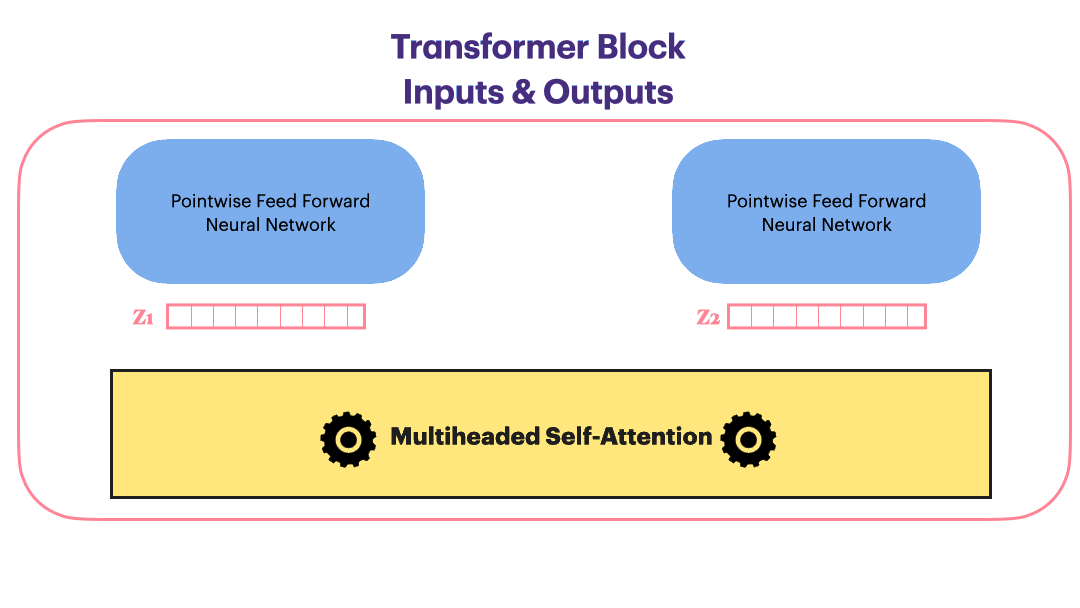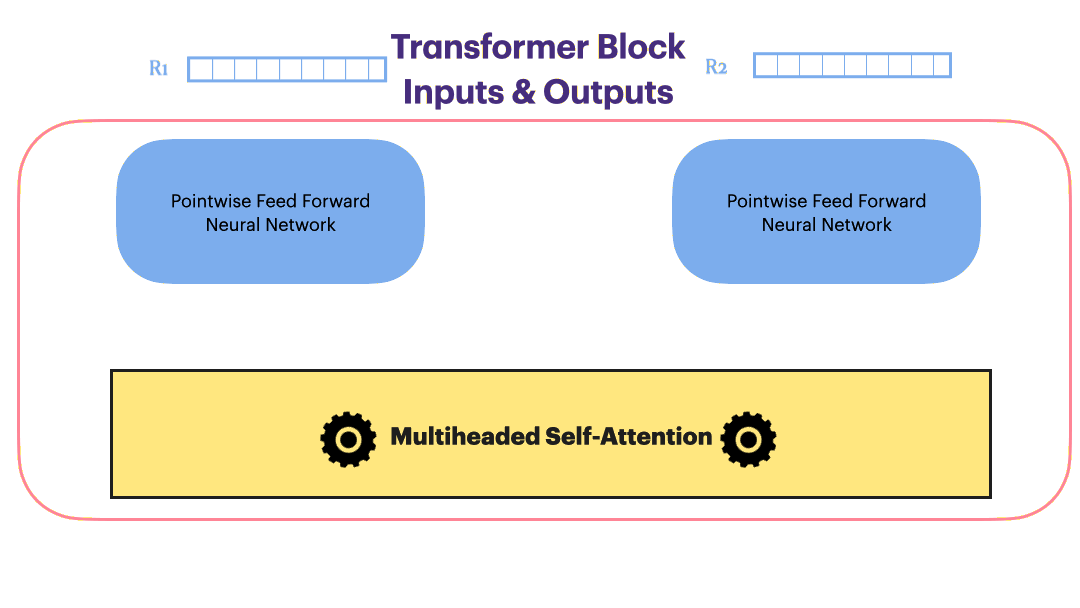
class MultiheadAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,nheads,dmodel,dropout=0.1):
super(MultiheadAttention,self).__init__()
assert dmodel % nheads ==0
self.dk = dmodel//nheads
self.nheads = nheads
#From the theory Wq linear layer should be (dmodel x dk)
#But in implementation (we're using dmodel x dmodel) we will breakdown Wq into h heads later.
#It can we shown that calculating 'nheads' small q_i's of BxLxdk dimension individually by feeding
#key, query, value of dimension BxLxdk each is equivalent to
#calculating 1 big Wq of BxLxdmodel dimension and feeding in large X (BxLxdmodel) to get a large Q (BxLxdmodel)
#then breaking Q into 'nheads' smaller q_i's of dimension BxLxdk each.
self.Wq = nn.Linear(dmodel,dmodel)
self.Wk = nn.Linear(dmodel,dmodel)
self.Wv = nn.Linear(dmodel,dmodel)
self.Wo = nn.Linear(dmodel,dmodel)
self.dropout_value = dropout
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p= dropout)
def forward(self,query,key,value,mask=None):
if mask is not None:
# Same mask applied to all of the nheads
mask.unsqueeze(1)
#Dim: q=k=v=x : (BxLxdmodel)
key,query,value = self.Wk(key), self.Wq(query), self.Wv(value) #k,q,v = (BxLxdmodel)
#Break k,q,v into nheads k_i's, q_i's and v_i's of dim (BxLxdk)
key = key.view(nbatches,-1,self.nheads,self.dk ) #(B,L,nheads,dk) (view -1: actual value for this dimension will be inferred so that the number of elements in the view matches the original number of elements.)
query = query.view(nbatches,-1,self.nheads,self.dk)
value = value.view(nbatches,-1,self.nheads,self.dk)
key = key.transpose(1,2) # (B,L,nheads,dk) --> (B,nheads,L,dk)
query = query.transpose(1,2)
value= value.transpose(1,2)
#Calculate self attention and enriched embedding z_i's.
#All z_i's are channeled together in 1 large z matrix below
z, self.attn = self_attention(query, key,value,mask,self.dropout_value) #z : (B,nheads,L,dk), attn: (B,nheads,L,L)
#Reshape z:(B,nheads,L,dk) -->z_concat (B,L,nheads*dk) to refelect the affect of concatenation as shown in figure
z_concat = z.transpose(1,2) #z:(B,nheads,L,dk) --> z_concat: (B,L,nheads,dk)
z_concat = z_concat.contiguous() #z_concat: (B,L,nheads,dk) --> z_concat: (1,B*L*nheads*dk)
z_concat = z_concat.view(nbatches, -1, self.nheads * self.dk) #z_concat: (1,B*L*nheads*dk) --> z_concat (B,L,nheads*dk)
#Project z_concat with linear layer (Wo) to get final enriched embedding z_enriched as shown in figure
#z_concat (B,L,nheads*dk) --> z_enriched(B,L,dmodel)
z_enriched = self.Wo(z_concat)
return z_enriched
Pointwise Feedforward Neural Network
$FFN(x) = max(0,xW_1+b_1)W_2 + b_2$
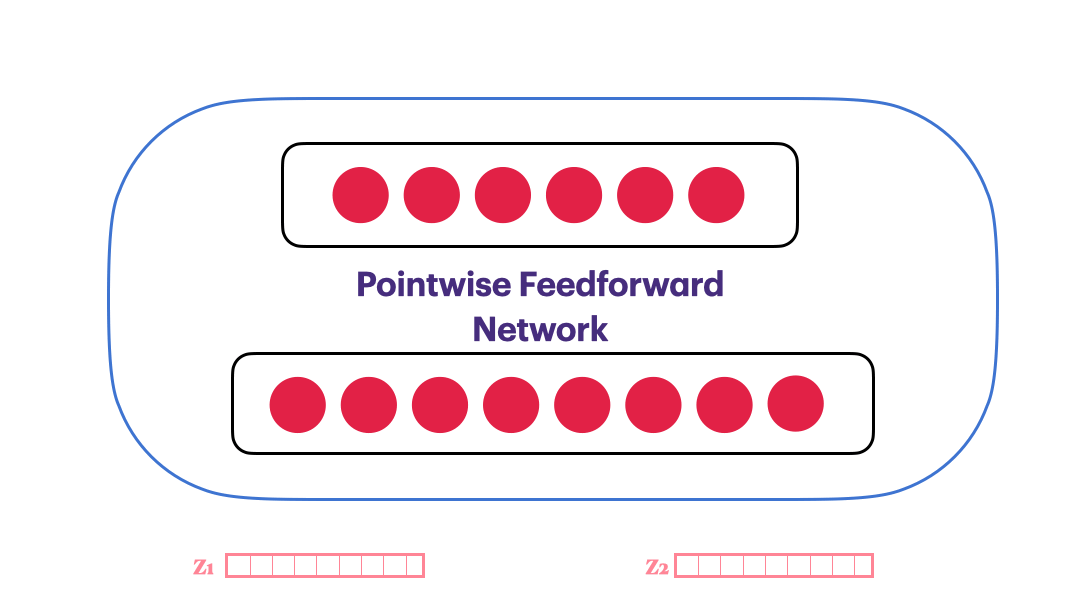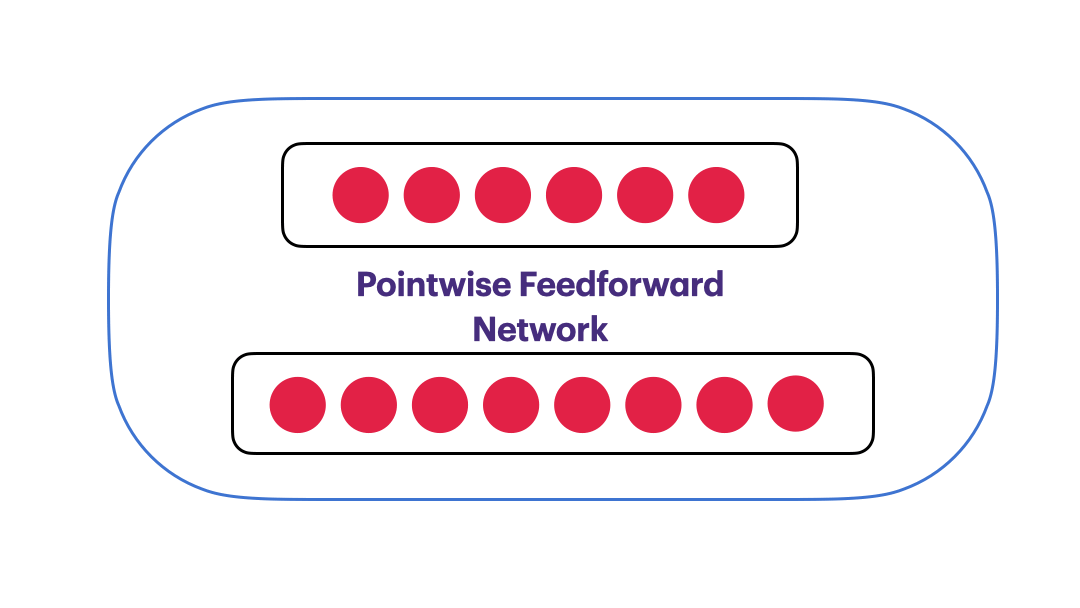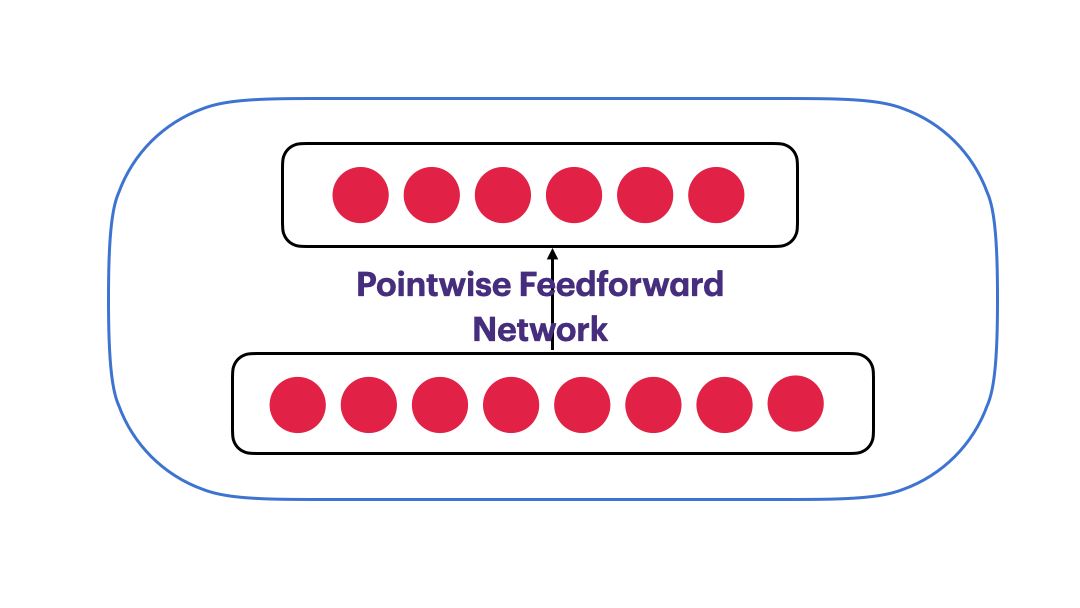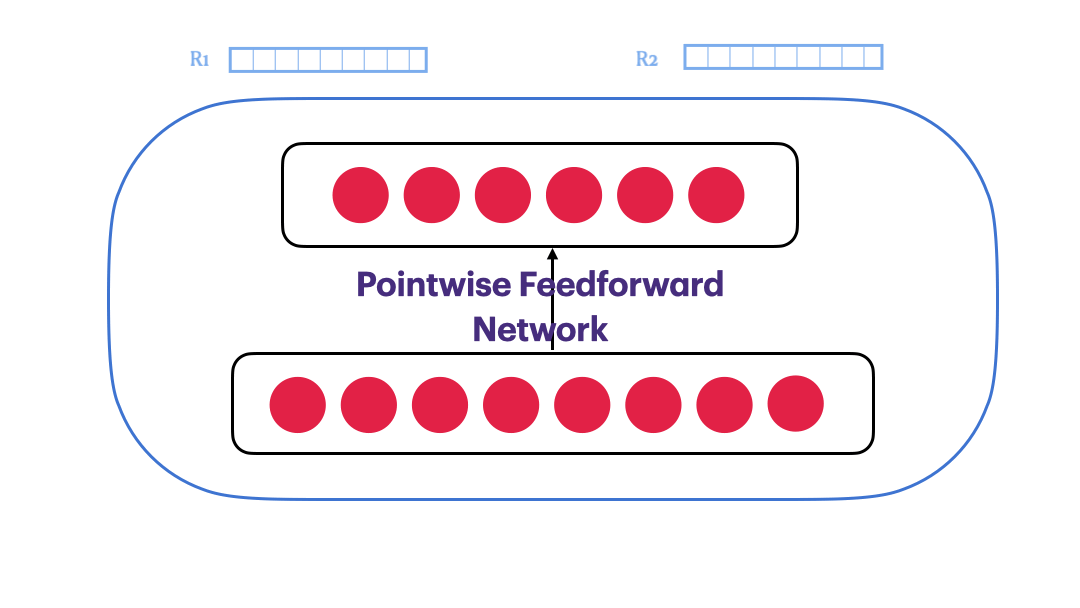
class PointwiseFeedForward(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,dmodel, d_linear,dropout = 0.2):
super(PointwiseFeedForward,self).__init__()
self.W1 = nn.Linear(dmodel,d_linear)
self.W2 = nn.Linear(d_linear, dmodel)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
def forward(x):
relu = F.relu(self.W1(x))
output = self.dropout(self.W2(x))
return output
LayerNorm
\(X=\{x_1,x_2......x_m\} \\ % Y =\{y_1,y_2......y_m\} \\ x_i = \{x_{i,1},x_{i,2},.........,x_{i,K}\}\)
LayerNorm normalizes each $x_i$ across all its (K) features such that each sample $x_i$ has 0 mean and unit variance.
\[\mu_i = \frac{1}{K}\sum_{k=1}^K x_{i,k} \\ \sigma_i^2 = \frac{1}{K}\sum_{k=1}^K (x_{i,k}-\mu_i)^2\] \[\hat{x}_{i,k}= \frac{x_{i,k}-\mu_i}{\sqrt{\sigma_i^2 + \epsilon}}\]And finally the output of a Layernorm layer $y_i = LN_{\beta,\gamma}(x_i)$
\[y_i = \gamma \hat{x_i} + \beta\]class LayerNorm(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,features,epsilon = 1e-9):
'features = number of features along which to normalize \
in the given input vector/matrix = dmodel'
super(LayerNorm,self).__init__()
self.gamma = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(features))
self.beta = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(features))
self.epsilon = epsilon
def forward(x):
#calculate mean and std across the last dimension.
#this will enforce that mean and std are calculated across
#all features of a fed in example.
mean = x.mean(-1)
std = x.std(-1)
x_hat = x-mean/(std+self.epsilon) #for numerical stability, we skip sqrt in denominator
output = self.gamma*x_hat + self.beta
return output
Residual Connection (Add & Norm)
Residual Connection followed by layerNorm
\[Add\_and\_Norm(Sublayer(x)) = LayerNorm(x+Dropout(Sublayer(x)))\]With the Residual connection and LayerNorm, the complete Transformer block looks as following 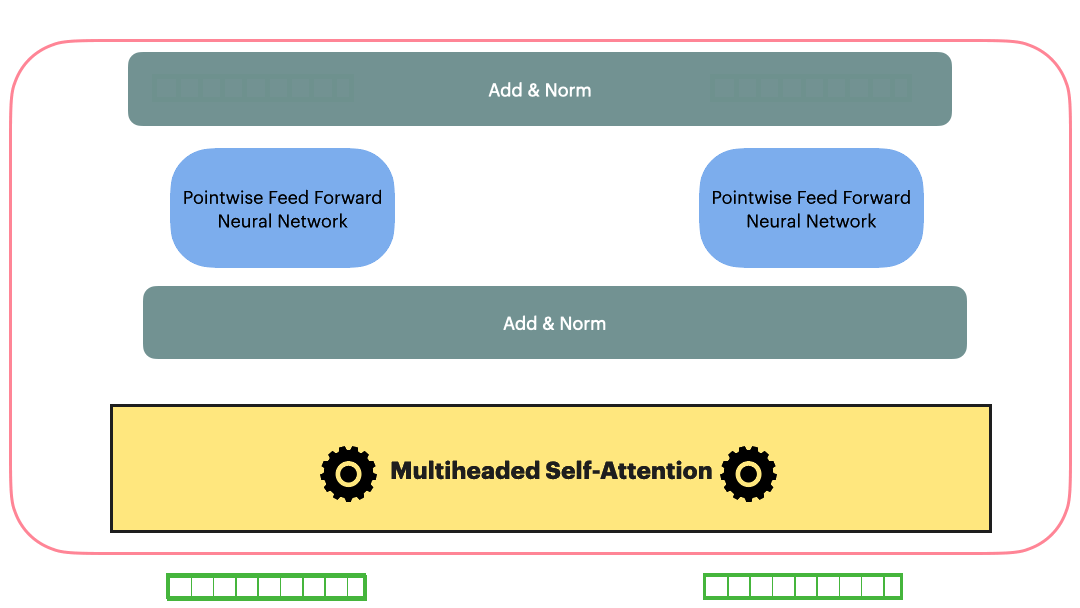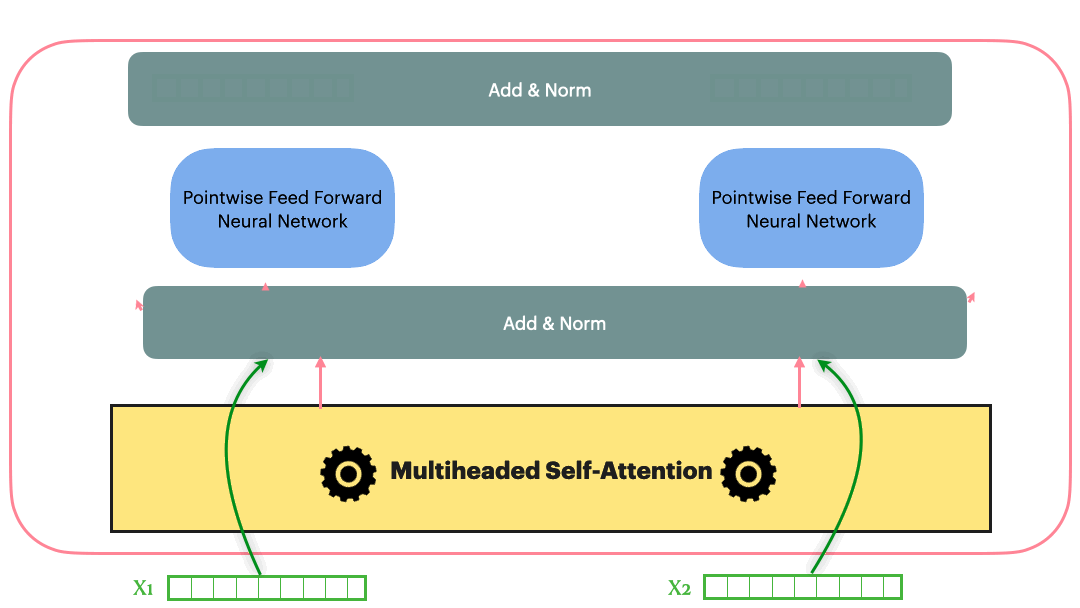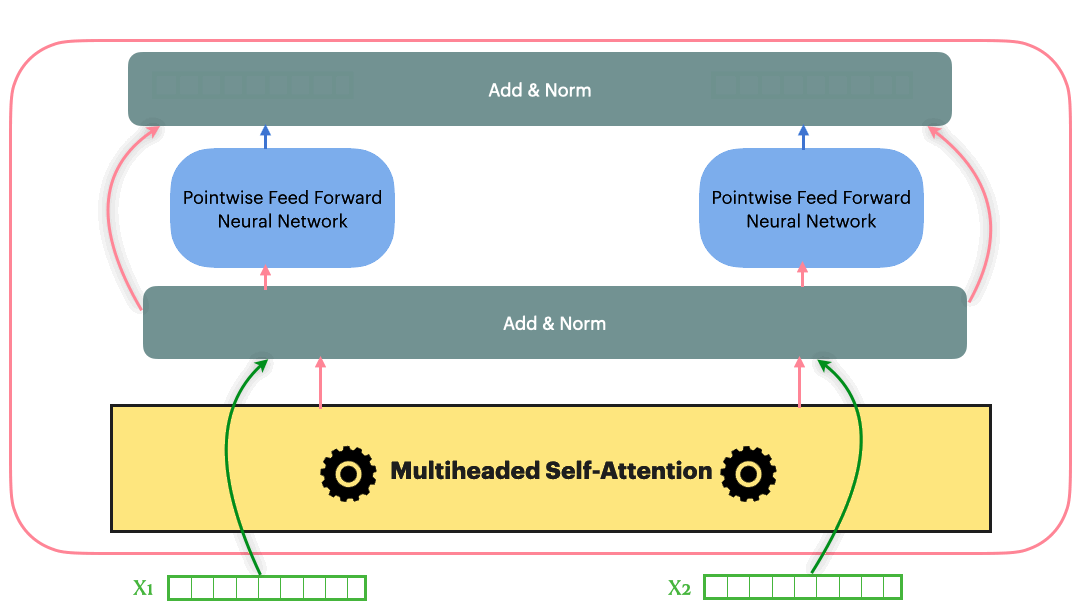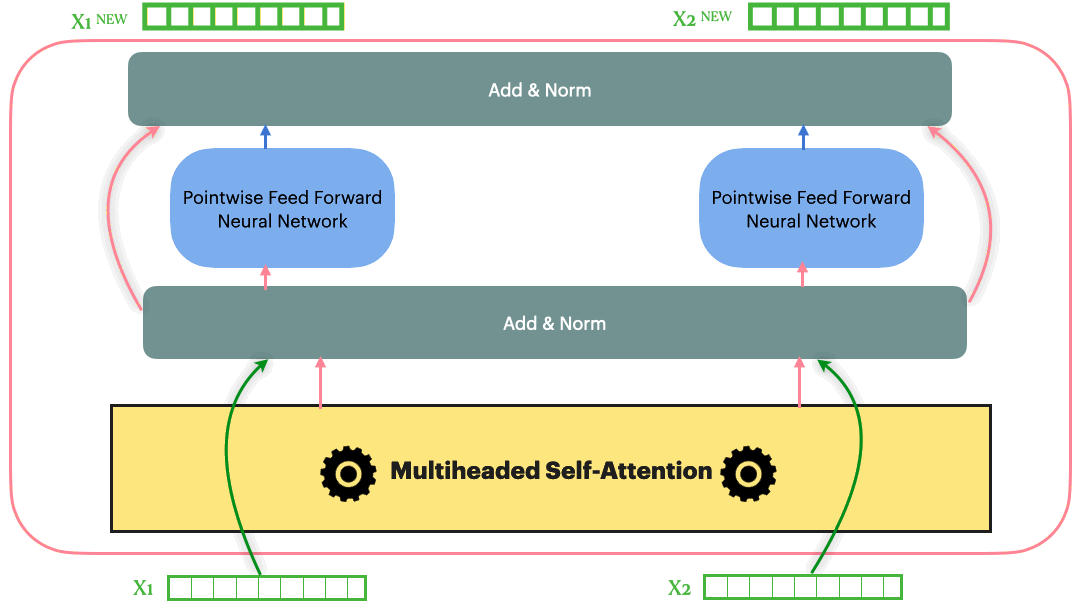
class AddandNorm(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,features,dropout=0.2,epsilon = 1e-9):
super(AddandNorm,self).__init__()
self.layernorm = LayerNorm(features,epsilon)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
def forward(self,x,sublayer_output):
return self.layernorm(x+self.dropout(sublayer_output))
Positional Embedding
Input representation: $\hspace{23mm}\textbf{X_input} \in R^{L \times dmodel}$
Positional Embedding: $\hspace{23mm}\textbf{P} \in R^{L \times dmodel}$
Updated Embedding: $\hspace{23mm}\textbf{X} = \textbf{X_input} + \textbf{P}$
Elements in $\textbf{P}$ are calculated as following \(p_{i,2j}= sin\bigg(\frac{i}{10000^{\frac{2j}{dmodel}}}\bigg) = sin(\theta)\)
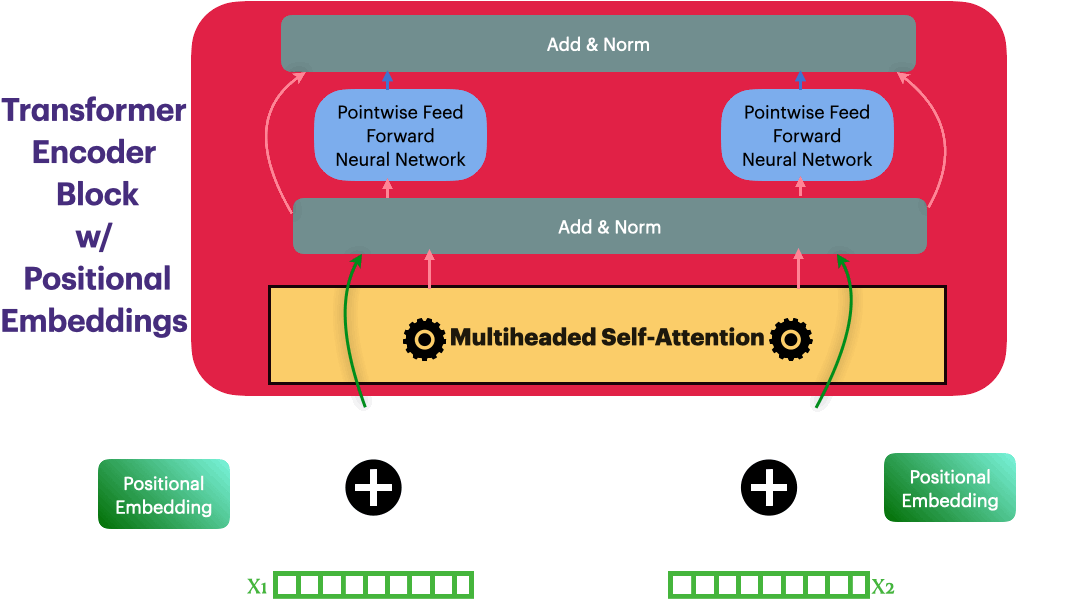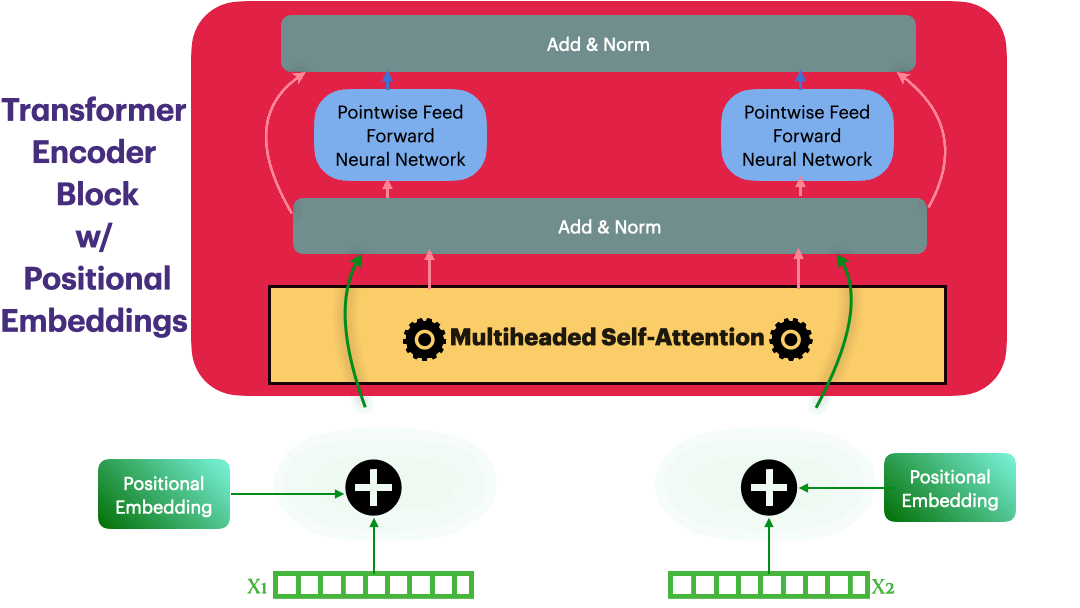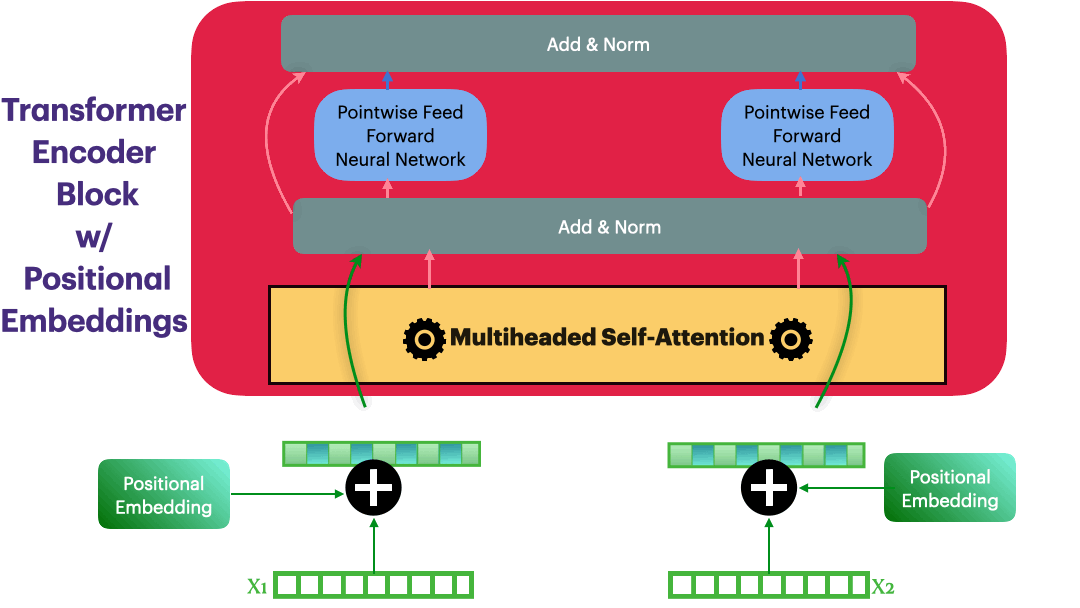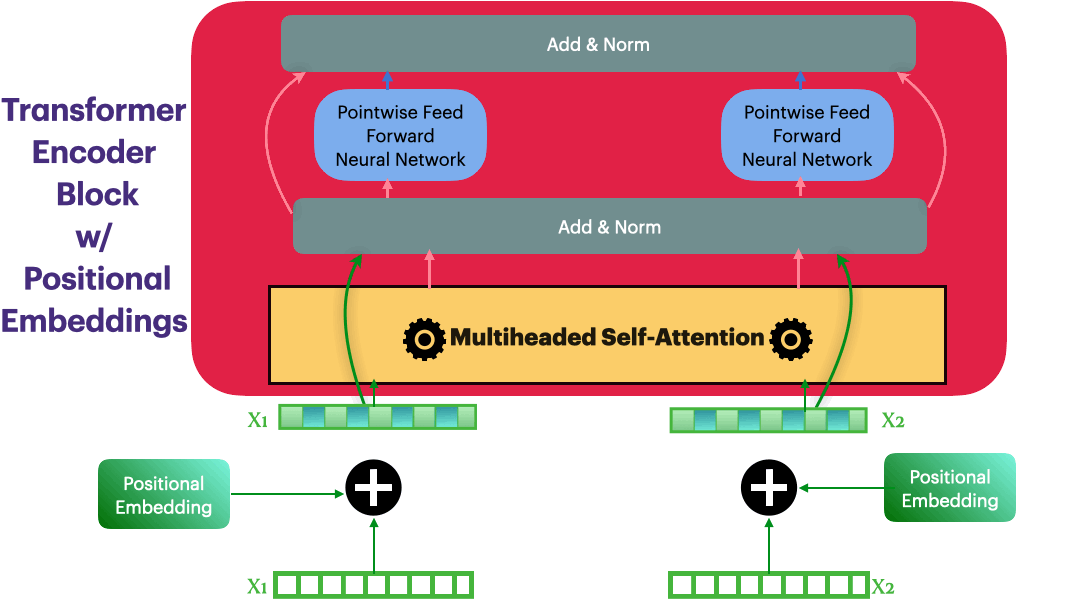
class PositionalEmbedding(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,dmodel,device,maxlen=10000,dropout=0.2):
super(PositionalEmbeddingitionalEmbedding,self).__init__()
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.device = device
#i is a max_len dimensional vector, so that we can store a positional embedding
#value corresponding to each token in sequence (Character in SMILES)
theta_numerator = torch.arange(max_len,dtype = torch.float32)
theta_denominator = torch.pow(10000,torch.arange(0,dmodel,2,dtype=torch.float32))/dmodel
theta = theta_numerator/theta_denominator
#Create a large P tensor to hold position embedding value for each token in the sequence
self.P = torch.zeros((maxlen,dmodel))
#Update even column ids in P with sin(theta) and odd column ids with cos(theta)
self.P[:,0::2] = sin(theta)
self.P[:,1::2] = cos(theta)
def forward(self,x):
# x.shape[1] gives the length of input sequence
x = x+self.P[:,x.shape[1],:]
return self.dropout(x)
Encoder Layer
We are ready to build a single encoder layer by combining Residual connection,
Layernorm, multiheaded attention block and position-wise feedforward network 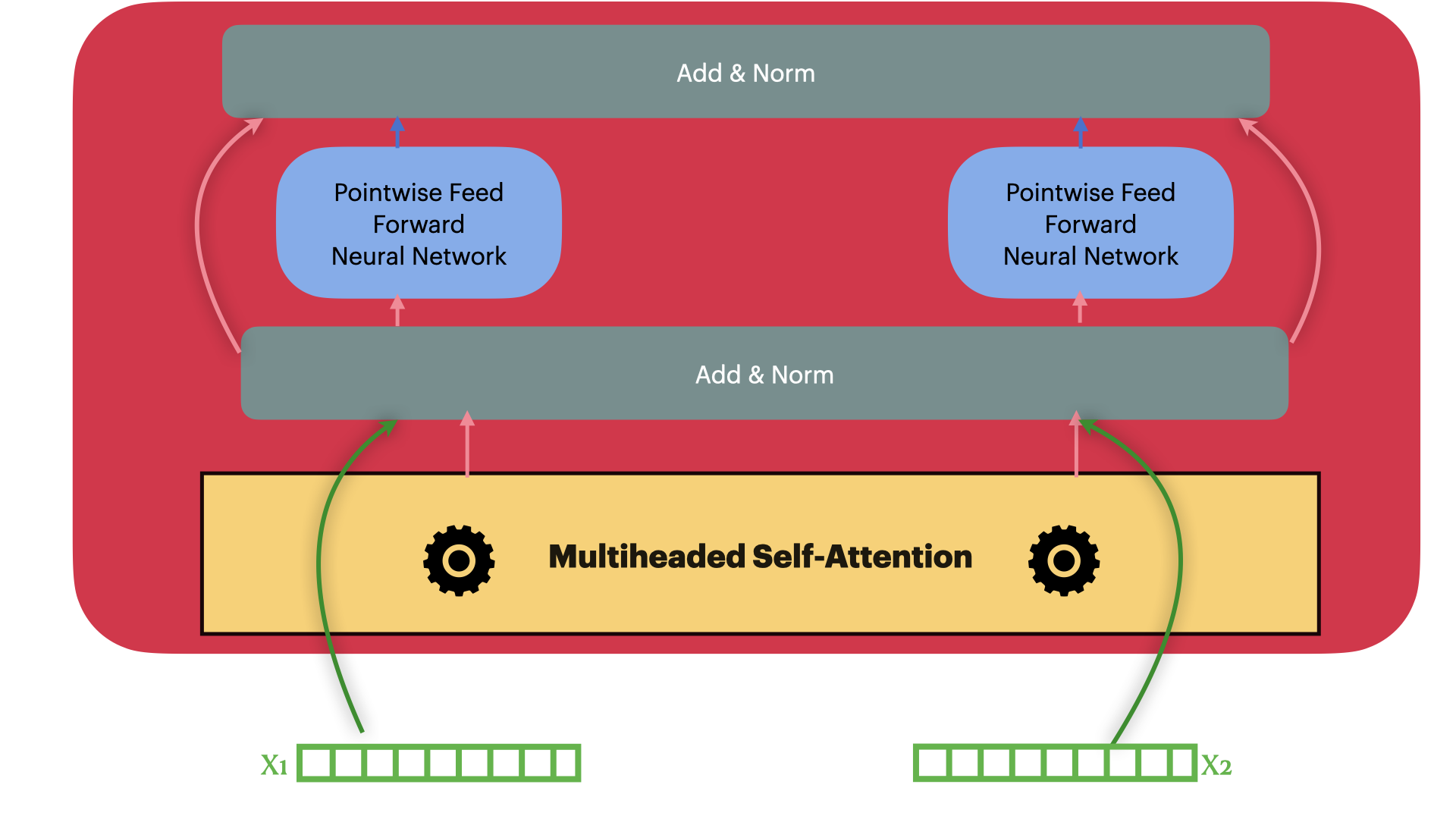
class EncoderLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,mask=None,nhead=8,dmodel=512,dlinear=1024,dropout=0.2):
super(EncoderLayer,self).__init__()
self.multihead_attn = MultiheadAttention(nheads,dmodel,dropout)
self.add_norm1 = AddandNorm(dmodel,dropout)
self.pw_ffn = PointwiseFeedForward(dmodel,dlinear,dropout)
self.add_norm2 = AddandNorm(dmodel,dropout)
def forward(self,x,mask=None):
'The input to the encoderlayer is either the embedding for first encoder layer \
or representions from previous layer. We use key=query=value = input (x) to feed \
into the multiheaded attention block within encoder layer'
multihead_attn_output = self.multihead_attn(x,x,x,mask)
addnorm1_out = self.add_norm1(x,multihead_attn_output)
pwffn_outputs = self.pw_ffn(addnorm1_out)
addnorm2_out = self.add_norm2(addnorm1_out,pwffn_outputs)
return addnorm2_out
Encoder (Stack of encoder layers)
Encoder stack is a sequential model with N encoder layers. Vaswani et al. used N=6 in their original paper.
class Encoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,device,src_vocab,nlayers=6,nhead=8,dmodel=512,
dlinear=1024,dropout=0.2):
super(Encoder,self).__init__()
self.dmodel = dmodel
self.encoder_stack = nn.Sequential()
self.embed = nn.Embedding(len(src_vocab),dmodel)
self.pos_embed = PositionalEmbedding(dmodel,device)
for i in range(nlayers):
self.encoder_stack.add_module("Encoder_Layer_"+str(i),
EncoderLayer(nhead,dmodel,dlinear,dropout))
def forward(self,x):
embedding = self.embed(x)
pos_embedding = self.pos_embed(embedding*math.sqrt(self.dmodel))
self.attention_weights = []
for layer in self.encoder_stack:
x = layer(x,mask)
self.attention_weights.append(layer.multihead_attn.attn)
return x
Decoder Layer
View 1 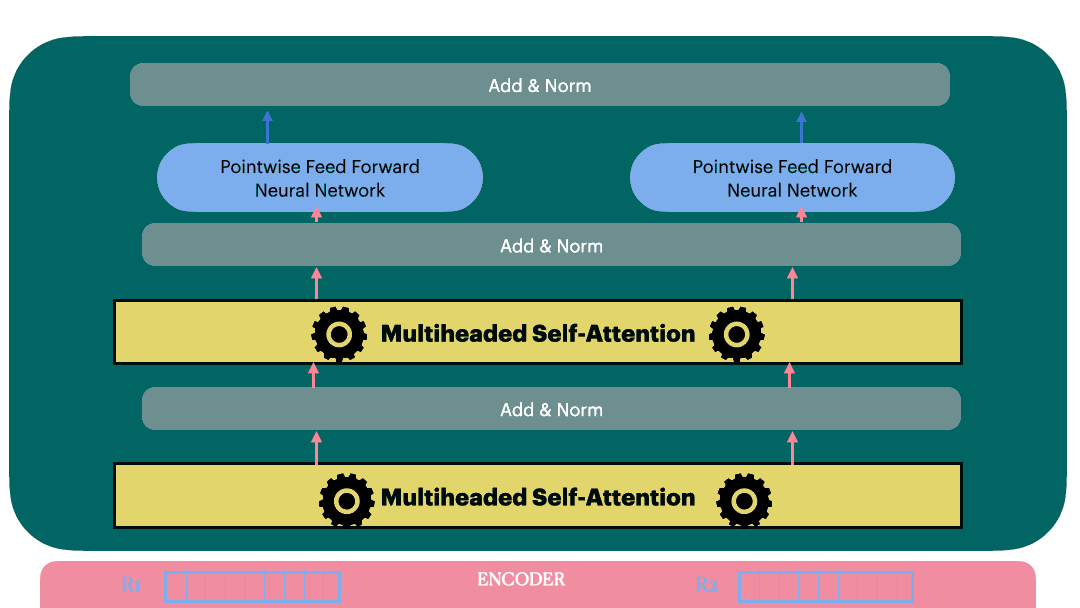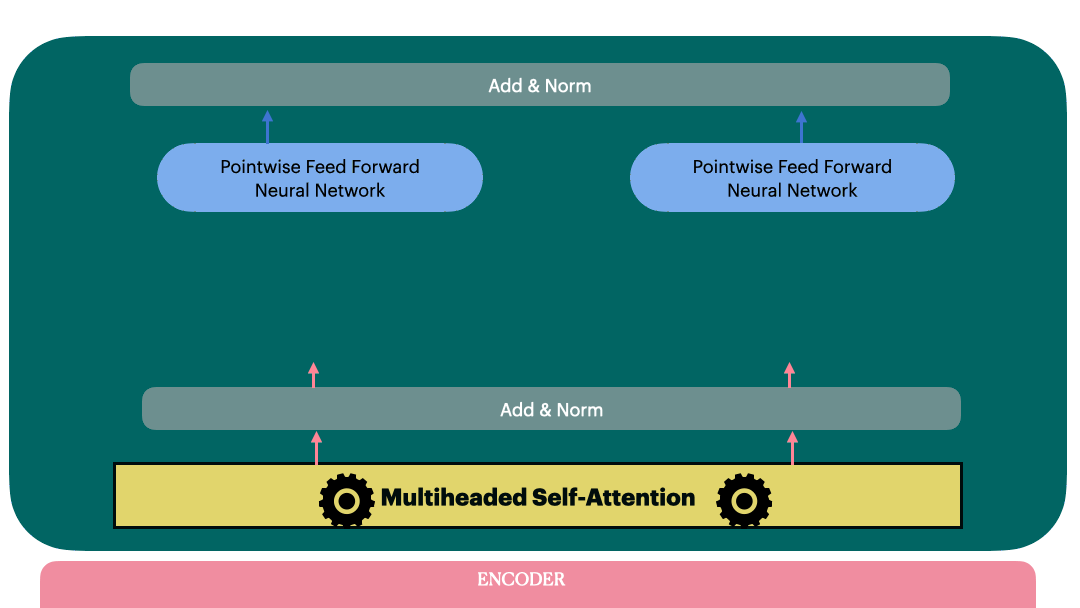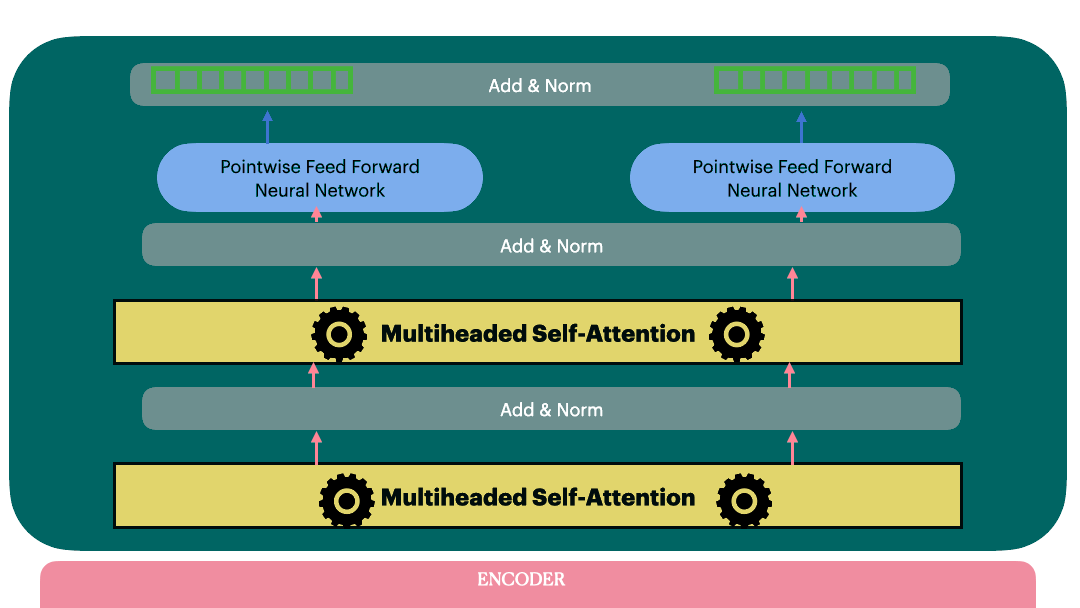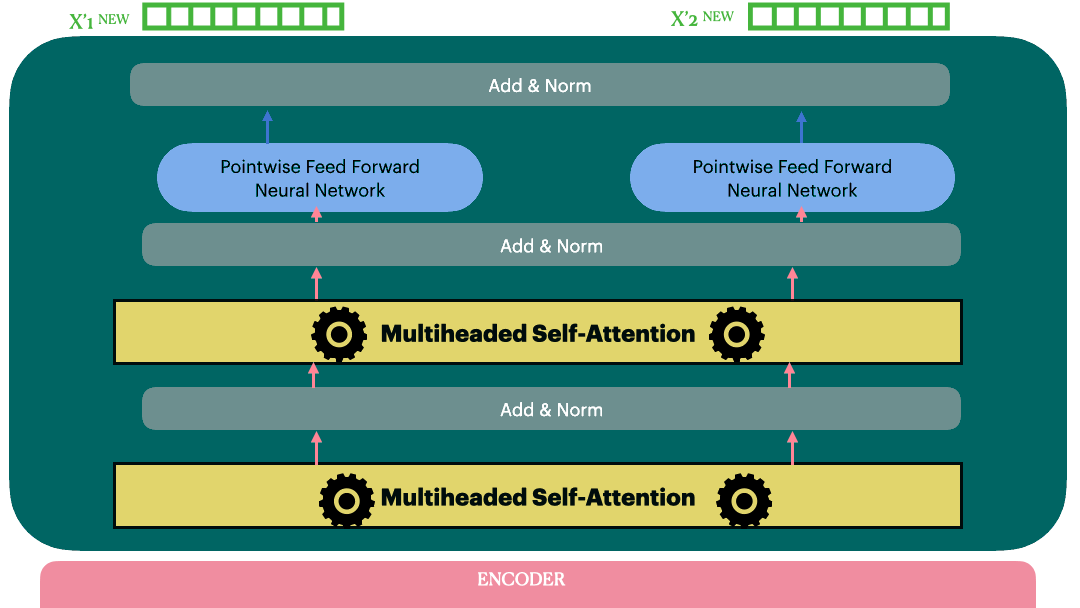
View 2 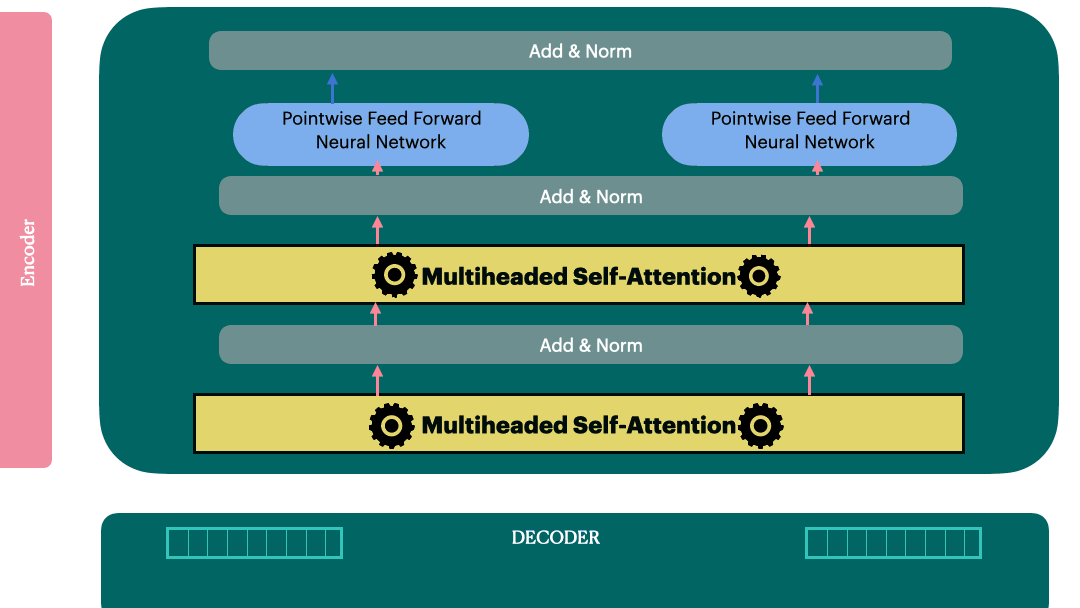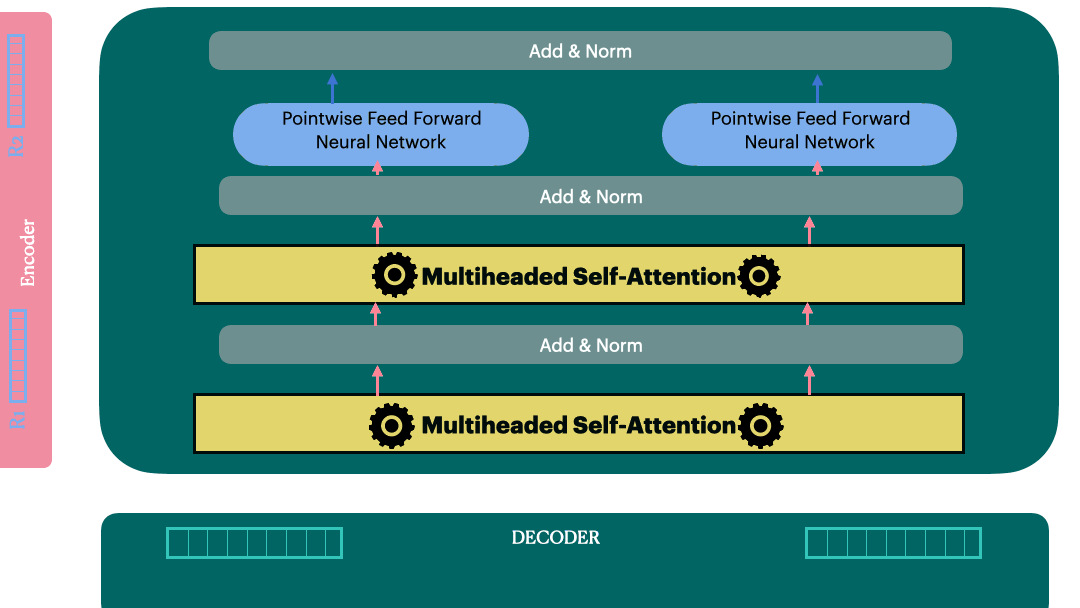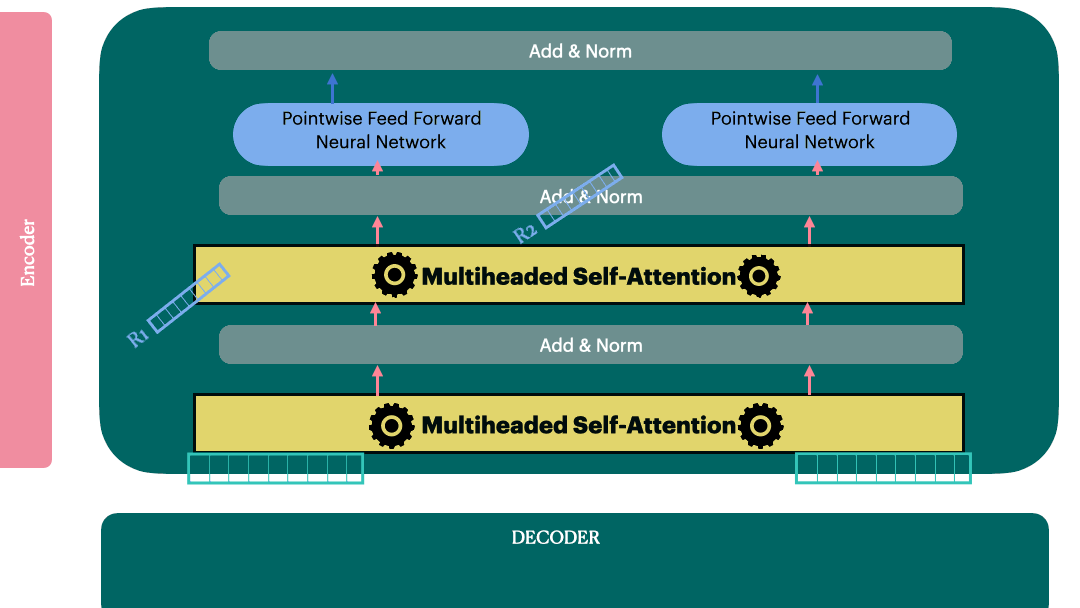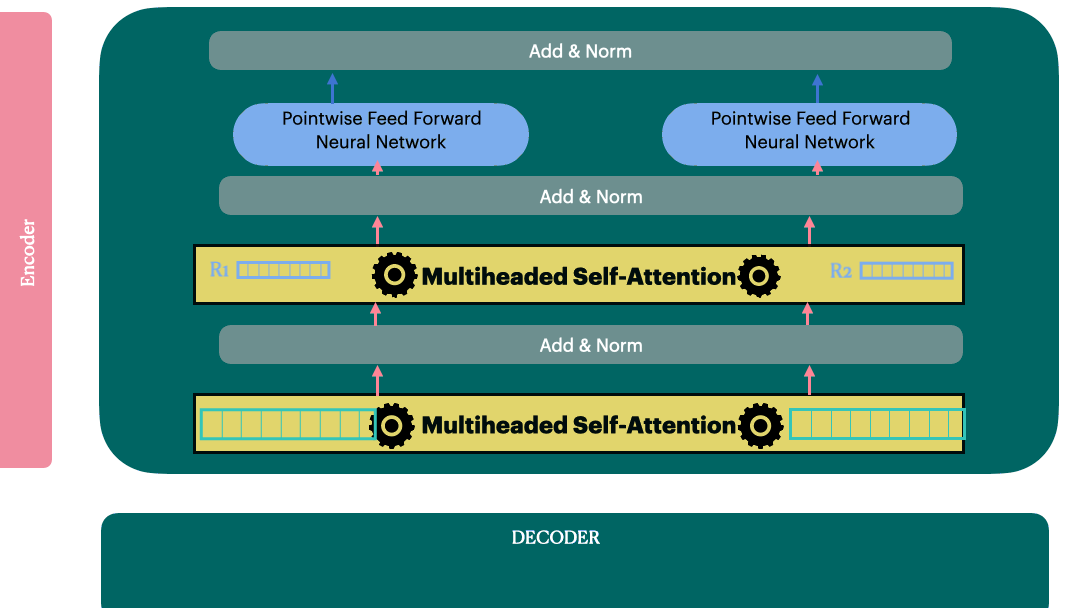
Autoregression
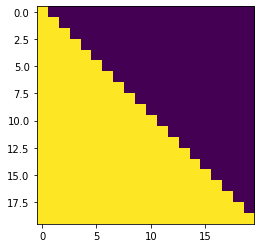
Mask out subsequent positions for decoder use
def autoregression_mask(nbatch,size):
"Mask out subsequent positions."
attn_shape = (nbatch, size, size)
autoregression_mask = np.triu(np.ones(attn_shape), k=1).astype('uint8')
return torch.from_numpy(autoregression_mask) == 0
print(autoregression_mask(1,20).shape)
plt.imshow(autoregression_mask(1,20).squeeze(0))
torch.Size([1, 20, 20])
<matplotlib.image.AxesImage at 0x7f2eba48b208>
Decoder layer
class DecoderLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,i,nheads=8,dmodel=512,dropout=0.2,dlinear=1024):
super(DecoderLayer,self).__init__()
self.i = i #identifier to distinguish decoder layers in stacked decoder
self.multihead_attn1 = MultiheadAttention(nheads,dmodel,dropout)
self.add_norm1 = AddandNorm(dmodel,dropout)
self.multihead_en_de = MultiheadAttention(nheads,dmodel,dropout)
self.add_norm2 = AddandNorm(dmodel,dropout)
self.pw_ffn = PointwiseFeedForward(dmodel,dlinear,dropout)
self.add_norm3 = AddandNorm(dmodel,dropout)
def forward(self,x,encoder_output,encoder_mask,decoder_state,time_step=0):
nbatch = x.shape[0]
if self.training:
decoder_mask = autoregression_mask(nbatch,self.dmodel) #(B,L,L)
else:
decoder_mask = None
if self.training:
#when training, decoder has access to the entire output sequence
#hence can take entire x (target sequence) as input. Obviously proper masking
#of target sequence is needed to stop the decoder from seeing future tokens
mulithead_attn1_output = self.multihead_attn1(x,x,x,decoder_mask)
else:
#when validating, decoder hasn't produced the word beyond the time step it is
#processing. Decoding happens one word at a time during validation.
#at t=0, input to multihead_attn1
#q,k,v = <bos> token,
#at t=1 and beyond, input to ith decoder block (from prev. decoder side) is whatever
#was predicted at prev. time step and the ith decoder block's state at t-1 timestep.
#See figure above
if time_step ==0:
mulithead_attn1_output = self.multihead_attn1(x,x,x,decoder_mask)
#update decoder state with current time step's state
decoder_state[self.i]= x
else:
decoder_query = x
decoder_key_value = torch.cat((decoder_state[self.i],x),dim=1)
mulithead_attn1_output = self.multihead_attn1(x,decoder_key_value,
decoder_key_value,decoder_mask)
#update decoder state with current time step's state
decoder_state[self.i]= decoder_key_value
addnorm1_out = self.add_norm1(x,mulithead_attn1_output)
key,value,query = encoder_output,encoder_output,addnorm1_out
multihead_en_de_output = self.multihead_en_de(query,key,value,encoder_mask)
addnorm2_out = self.add_norm2(addnorm1_out,multihead_en_de_output)
pwffn_outputs = self.pw_ffn(addnorm2_out)
addnorm3_out = self.add_norm2(addnorm2_out,pwffn_outputs)
return addnorm3_out,decoder_state
Decoder
Decoder stack is also a sequential model like encoder with N layers. Vaswani et al. used N=6 in their original paper.
class Decoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,device,tgt_vocab,nlayers=6,nhead=8,dmodel=512,
dlinear=1024,dropout=0.2):
super(Decoder,self).__init__()
self.dmodel = dmodel
self.nlayers = nlayers
self.embed = nn.Embedding(len(tgt_vocab),dmodel)
self.pos_embed = PositionalEmbedding(dmodel,device)
self.decoder_stack = nn.Sequential()
for i in range(nlayers):
self.decoder_stack.add_module("Decoder_Layer_"+str(i),
DecoderLayer(i,nhead,dmodel,dropout,dlinear))
self.dense = nn.Linear(dmodel,len(tgt_vocab))
def forward(self,x,encoder_output,encoder_mask,decoder_state,time_step=0):
embedding = self.embed(x)
pos_embedding = self.pos_embed(embedding*math.sqrt(self.dmodel))
#To save attention weights from both multiheaded attention layers
#for later visualization
self.att_wts_de,self.att_wts_en_de = [],[]
for layer in self.encoder_stack:
x,decoder_state = layer(x,encoder_output,encoder_mask,decoder_state,time_step)
self.att_wts_de.append(layer.multihead_attn1.attn)
self.att_wts_en_de.append(layer.multihead_en_de.attn)
return dense(x),decoder_state
Transformer Network
class Transformer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,encoder,decoder):
super(Transformer,self).__init__()
self.encoder = encoder
self.decoder = decoder
def forward(self,src_input,src_mask,tgt_input,decoder_state,time_step):
encoder_output = encoder(src_input)
decoder_output,decoder_state = decoder(tgt_input,encoder_output,
encoder_mask,decoder_state,time_step)
encoder = Encoder(device,src_vocab,nlayers=6,nhead=8,dmodel=512,
dlinear=1024,dropout=0.2)
decoder = Decoder(device,tgt_vocab,nlayers=6,nhead=8,dmodel=512,
dlinear=1024,dropout=0.2)
trfm_network = Transformer(encoder,decoder)

 Encode-Attend-Decode Architecture
Encode-Attend-Decode Architecture
Leave a Comment